What is LOAS?
LOAS is a collection of scripts that are used to perform various offensive operations on macOS
Living Off the Orchard: Apple Script is a library of AppleScript and JXA tests mapped to the MITRE ATT&CK® framework. Security teams can use LOAS to quickly, portably, and reproducibly test their macOS environments using multiple execution methods, each generating different endpoint security logs.
Executing Apple Script
This project provides multiple ways to execute Apple Script. You can execute it via CLI, osascript, Swift, Applet, or run the binary directly.
These execution methods are documented in the Red Canary Threat Detection Report. Much of the work was done by them and this documentation expands on it.
The GitHub releases page provides all of these different files for each test.
If you would like to compile the files yourself, install uv and then use the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/cyberbuff/loas.git
cd loas
uv sync
uv run main.py buildEach of these methods generate different set of logs based on the execution tool.
The below sample Endpoint Security logs are gathered using Mac Monitor for each of the execution methods for getting the clipboard content.
osascript CLI
This is the simplest way to execute commands from this repository.
osascript -e "the clipboard"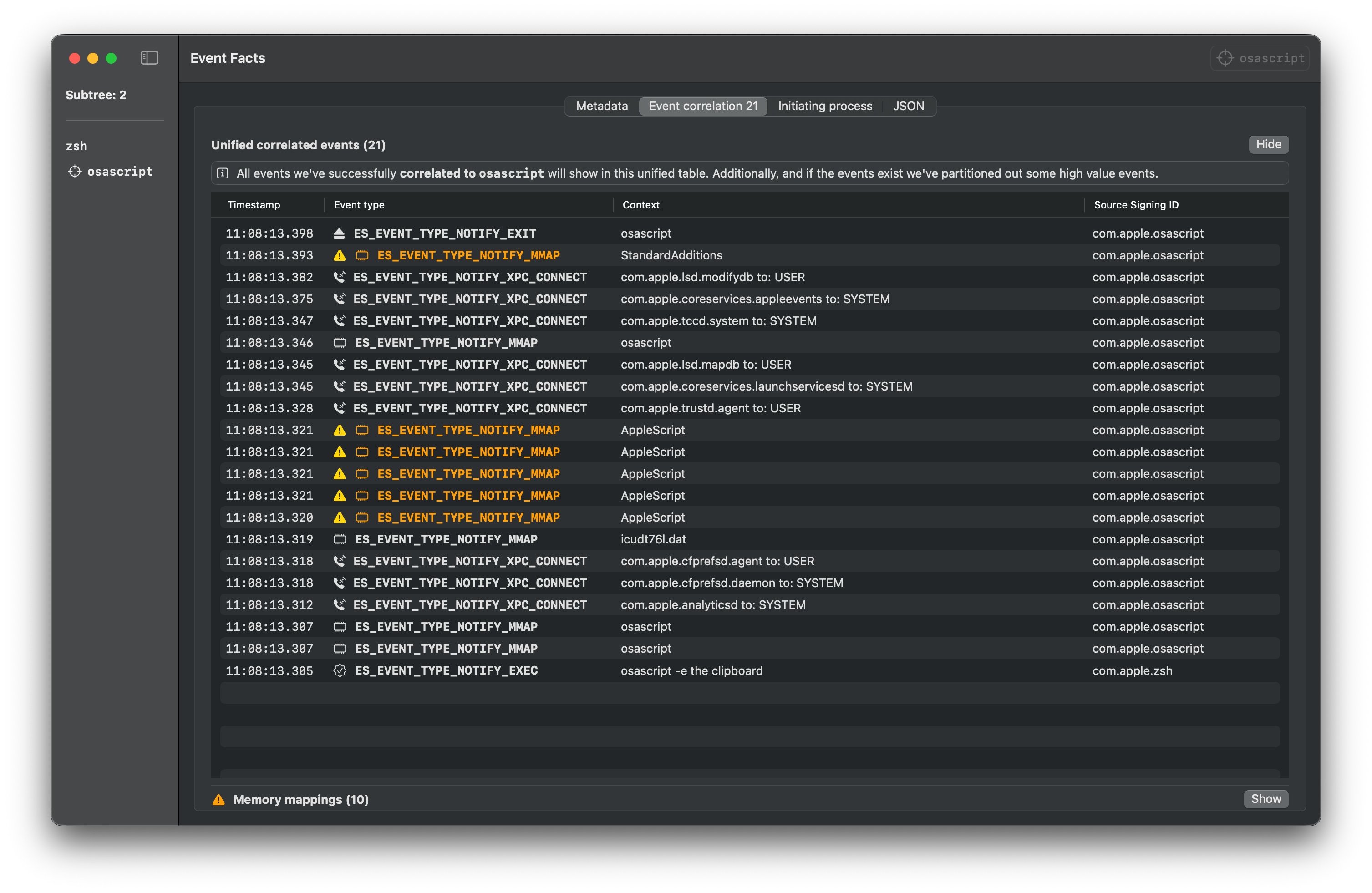
Script
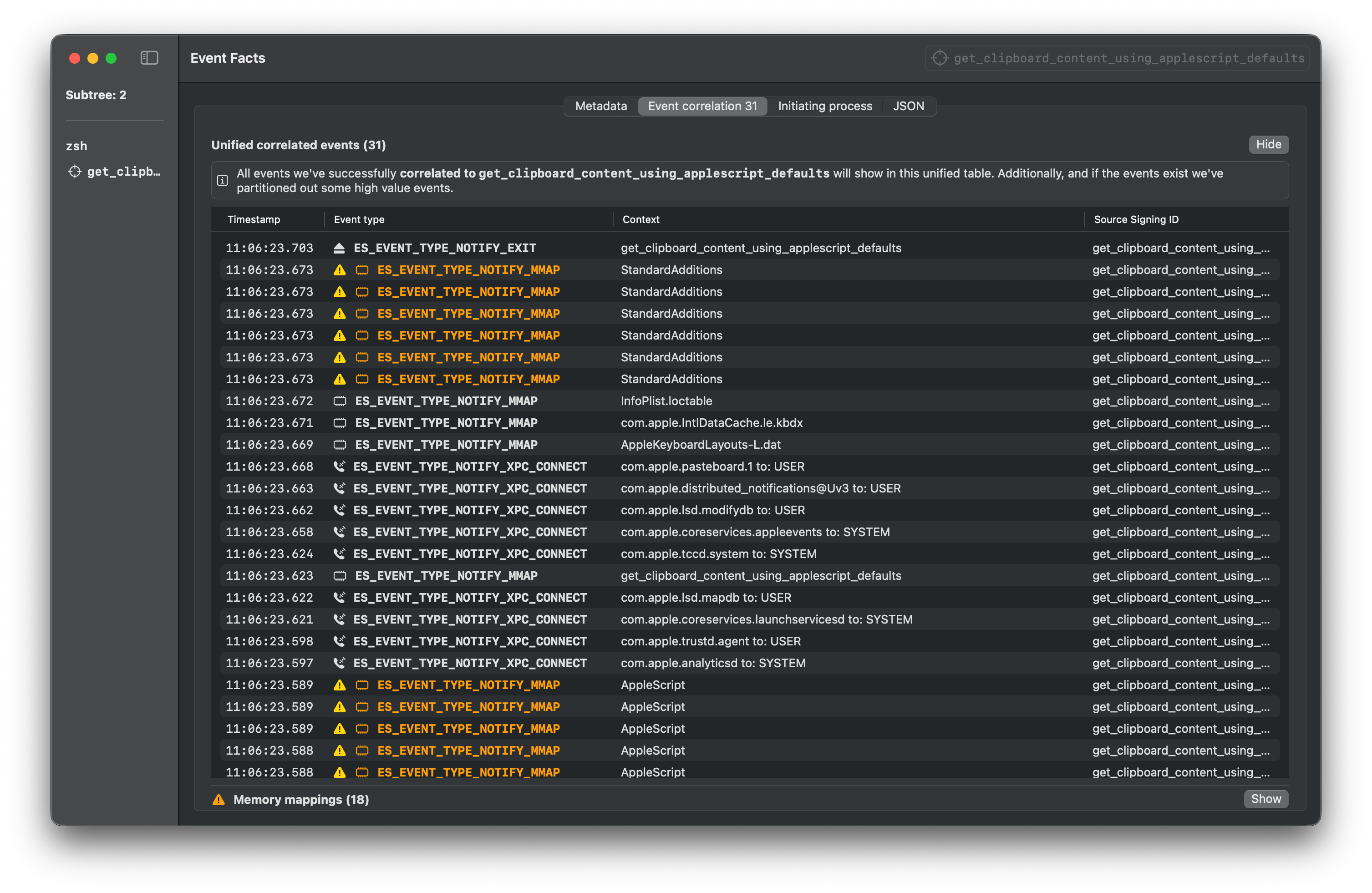
Download the script from the releases page and execute it with osascript.
osascript get_clipboard_content_using_applescript_defaults.scpt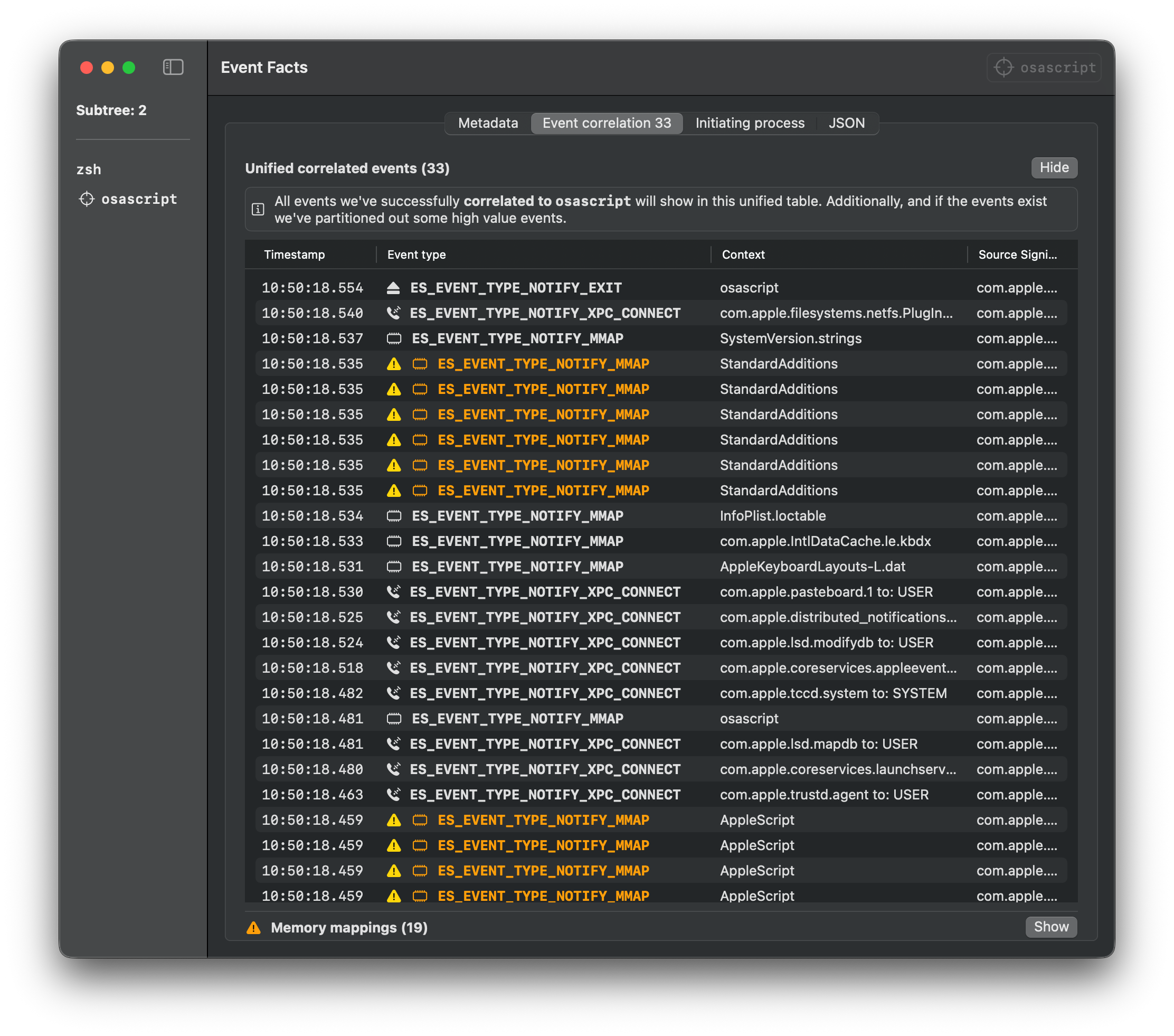
Swift
Download the Swift file from the releases page and execute it with Swift.
Note: You might need to install XCode Developer Tools to run Swift files.
swift get_clipboard_content_using_applescript_defaults.swift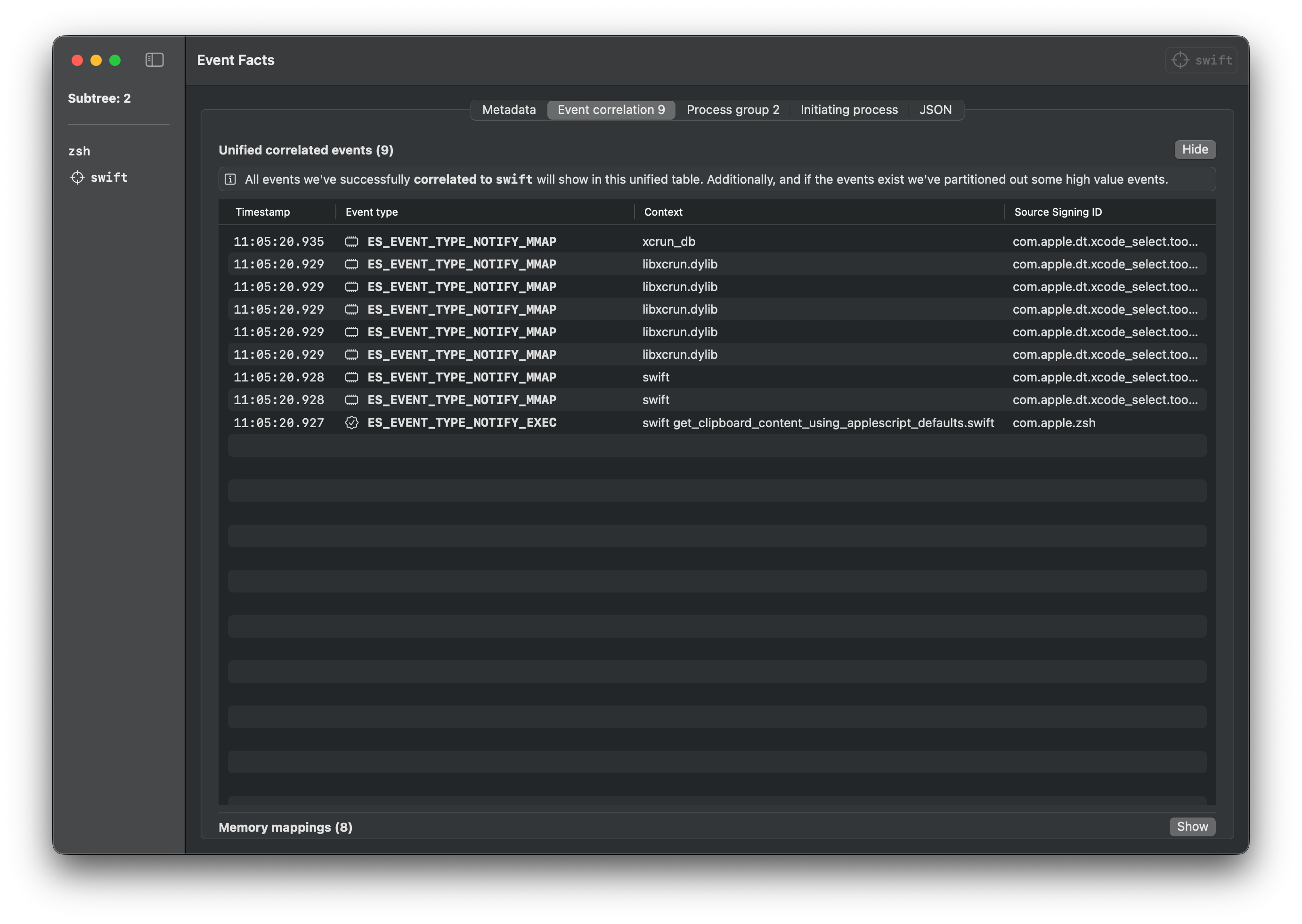
Applet
Download the .app file from the releases page and execute it.
open -n get_clipboard_content_using_applescript_defaults.app
Binary
Download the binary from the releases page and execute it.
./get_clipboard_content_using_applescript_defaults